The choice of the best mobile application development approach is one of the most decisive choices made in business in the current times. The ever-lasting controversy between native app development and cross-platform development impacts all aspects of the project schedule up to the success measure of the long-term strategy. In this in-depth discussion, I will explain the key factors that should be considered so that you can make a wise decision that is relevant to your particular project objectives and corporate objectives.
The Current State of Mobile Application Development
The current state of the digital ecosystem includes more than 7.1 billion mobile device users all around the globe and mobile applications contribute to the record-breaking revenue streams in industries. The strategic decision between native application development and cross platform development goes well beyond the technical preferences of your choice, it actually defines how your product will position itself in the market, end-user experience and scalability capabilities.
Native development involves the development of platform-specific applications based on special programming languages and development environments. On the other hand, cross-platform development allows a team to develop applications, which can run on different operating systems without any issues, based on the same codebase and specialized frameworks.
Native App Development: Platform-Centric Excellence
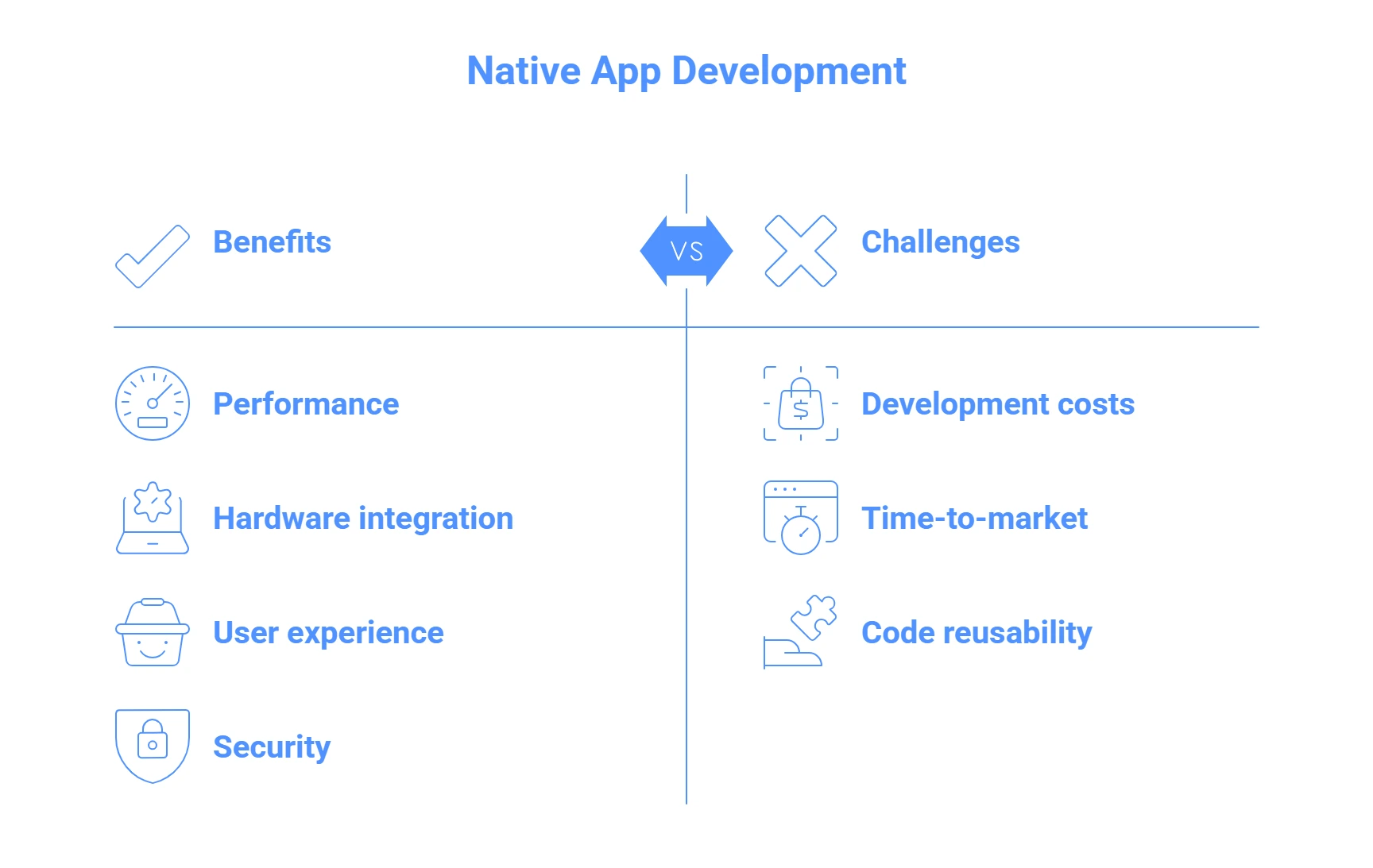
Native app development is the accuracy-based development of a mobile application. This approach necessitates the solo creation of apps on each of the target platforms, with platform-specific documents and programming languages, Swift or Objective-C when developing iOS applications, and Java or Kotlin when creating Android applications.
Core Benefits of Native Development
Performance optimization could become the distinguishing feature of native apps. These applications are in direct contact with operating system APIs and hardware subunits, and they provide superior application speed which is always faster than alternative development solutions. There are increased response times, improved interactions, and efficient use of resources by users.
Hardware integration capabilities make native applications distinguish themselves among their counterparts. These applications are able to utilize the advanced features of the devices such as high-quality camera features, accurate location, biometric sensors, and platform-specific APIs without sacrificing performance or compatibility.
Superior user experience design is another inherent strength. Naturally, native applications are designed to fit the platform design principles (i.e. Google Material design on Android and Apple Human interface guidelines on iOS), producing an intuitive, familiar experience that appeals to the customers established interaction patterns.
Enhanced security native development is preferred by the protocols especially in applications that handle sensitive user data. Native applications can use the platform-based security frameworks, encryption and authentication without adding more layers of abstraction that may expose vulnerabilities.
Native Development Challenges
Improved development costs present the greatest impediment to native growth. The development of individual applications on the iOS and Android platforms fundamentally doubles the investments in the development resources, specialized knowledge, and continuous work on maintenance.
Extended time-to-market cycles pose great competitive disadvantages. The cost of building several-platform specific applications necessarily takes a longer period of time compared to building unified solutions thus may force businesses to lose vital market opportunities or competitive gains.
Limited code reusability implies that business logic, implementations of features and functionality need to be recorded on each platform, which increases the chances of inconsistencies and raises the complexity of maintenance in the long term.
Cross-Platform Development: Unified Solution Architecture
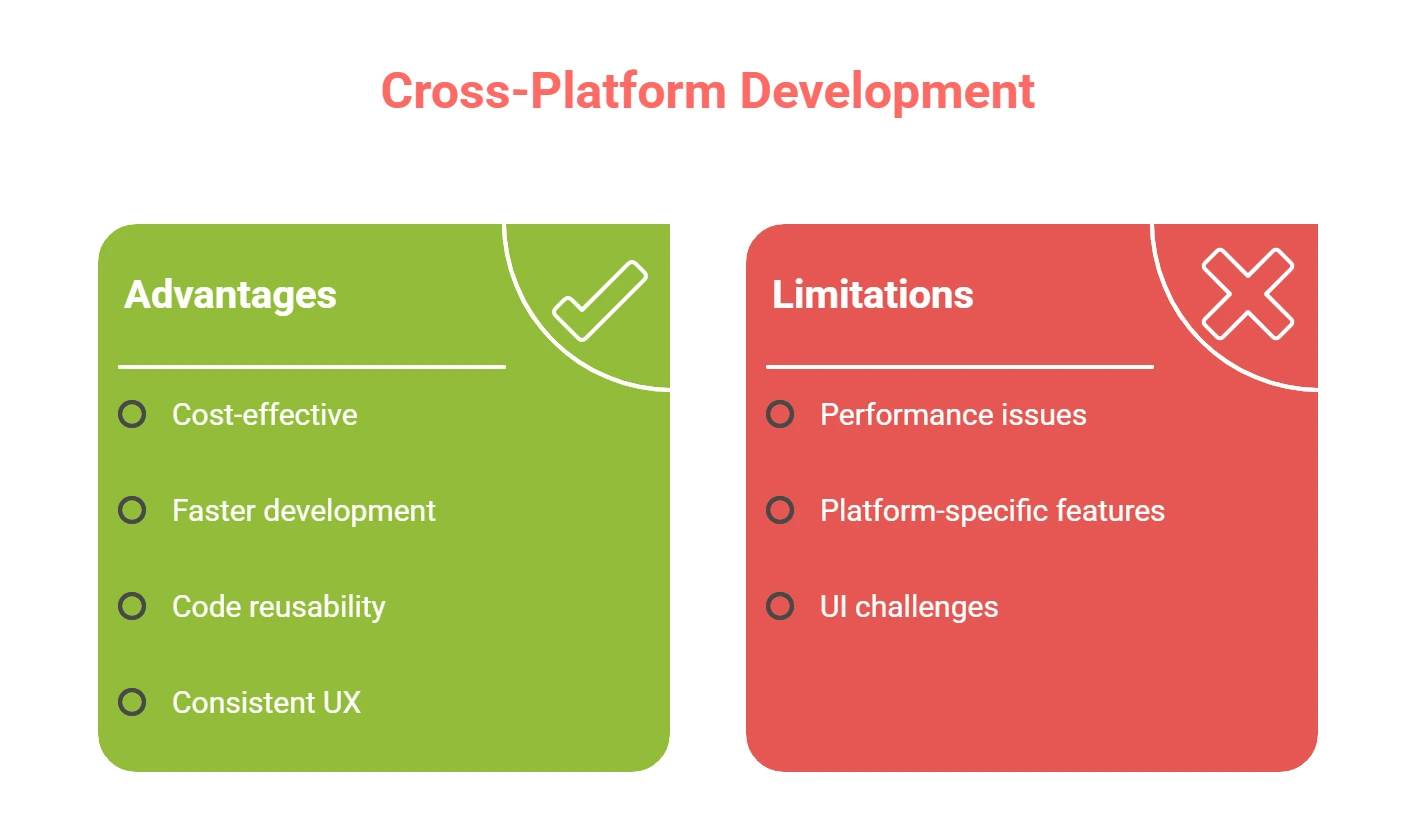
Mobile development economics with cross-platform application development frameworks such as React Native, Flutter, Xamarin, and Ionic have revolutionized mobile development. This method allows development teams to develop applications that can operate on many different platforms but share a common and single codebase.
Cross-Platform Development Advantages
Significant cost efficiency represents the most immediate benefit of cross-platform approaches. Organizations typically reduce development expenses by 35-55% compared to native development by eliminating duplicate development efforts and streamlining resource allocation.
Accelerated development timelines facilitate a high time-to-market. The cross-platform frameworks enable the teams to design, create and implement an application faster than in traditional native applications, which is very vital in terms of competitive advantage in rapidly changing markets.
Maximized code reusability maximizes the efficiency of development through the lifecycle of the project. Shared elements, implementations of business logic, and user interface elements minimize the duplication and ensure that all targeted platforms have the same functionality.
Standardized user experience across facilitates platform conformity and eases the user onboarding process. Cross-platform applications provide a consistent functionality as well as visual appearance irrespective of whether the user uses a particular device or operating system.
Cross-Platform Development Limitations
Performance constraints still are an important consideration to cross-platform applications. The abstraction layers required to have multi-platform compatibility may cause performance overhead, especially for graphics-intensive applications or computationally-intensive features.
Platform-specific feature capabilities limitations can either block access to some high-level functionality of the device, or may involve more effort to make it a specialized one. Although modern cross-platform frameworks have overcome a large number of historical shortcomings, there are still capabilities that are state-of-the-art, which might need native implementation strategies.
User interface problems with design continue as efforts are made to design interfaces that feel native on various platforms and are enabled by a common codebase. This frequently involves compromises in design or extra platform-specific customization work.
Performance Analysis: Quantitative Comparisons
The latest performance benchmarking research proves that there are quantifiable differences in development approaches. Native programs always load with an average of 1.8 seconds whereas cross-platform programs take 3.2 seconds to perform the same function. Applications that are processing-intensive demonstrate that native applications are about 35 percent faster in executing their computation-intensive operations than cross-platform implementations.
Contemporary cross-platform frameworks however have minimised these performance disparities significantly. The direct compile of Flutter and the architectural enhancements of React Native have enabled cross-platform application performance to be within the range of acceptable performance of most business applications and consumer facing products.
Security and Maintenance Considerations
Securing criteria tend to affect the choice of development method, particularly where the application is dealing with financial data or personal information or confidential business information. Development of native apps will allow direct access to platform-specific implementation of security, implementation of encryption using hardware and elaborate authentication without extra layers of complexity.
Cross-platform approaches are much more efficient in terms of maintenance. Once, updates, additions of features, and resolving of bugs can be implemented and deployed on all the supported platforms reducing the overhead of operation and providing similar end user experiences. Native applications need to have their own maintenance per platform, which may lead to higher costs and complexity of operation in the long run.
Strategic Decision Framework
The best decision between developing a native app and cross-platform one is based on the prudent consideration of the project peculiarities and limitations faced by the organization. Take native development approaches if:
-
The level of app performance can directly affect the user satisfaction.
-
There must be large-scale hardware integration.
-
High level security conditions cannot be compromised.
-
Competitive advantages are the platform specific features.
-
Higher start-up investments are supported by the development budget.
-
Specialized knowledge of platforms is easily accessible.
Choose cross platform development approaches in case:
-
The cost of development has to be optimized.
-
Time to market Competitive advantages.
-
There is high value to the organization with code reusability.
-
The strategic importance of maintenance efficiency is obvious.
-
Team experience conforms with cross-platform technologies.
-
Features that are business-critical are platform-specific.
Emerging Trends and Future Developments
The mobile application development environment keeps changing at a very high rate and cross-platform ecosystems are getting more sophisticated and performance optimized. The use of Flutter has been increasing exponentially, especially by companies in need of pixel perfection user interfaces and high performance optimization. React Native is an app that is well represented in the market particularly in companies that already have existing knowledge in JavaScript and those that have hastened development demands.
Progressive Web Applications (PWAs) are the latest alternative, which uses the web technologies to provide an experience of an app but with a minimum level of complexity. Although they cannot be applied to every application, PWAs can offer effective solutions to the teams that need a wide platform coverage with a minimum of resource allocation.
Hybrid approaches to development are emerging, which mix cross-platform frameworks to form the base functionality with native implementations of specialized functionality. This is a moderate stance that seeks to have the advantages of both strategies and reduce their shortcomings.
Conclusion: Strategic Alignment for Project Success
The choice of native app development or cross platform development should be very considerate of the technical requirements, business goals, and resource limitation. Native development is the best choice to use when performance optimization, security, and platform specific capabilities are the key factors, and cross platform methods offer the benefits of cost-efficiency, development speed and ease of maintenance.
Effective project results are based on the terms of careful assessment of user specifications, technical limitations, cost concerns, and strategic goals. The most common practice is to use flexible solutions that take the form of cross platform frameworks in which core functionality is implemented using the frameworks and then specialized functionalities are implemented as native features when it is necessary to be able to provide the performance or platform integration demands.
The decision criterion can change as the cross-platform frameworks themselves are maturing and the performance differentials keep decreasing. Nevertheless, the underlying trade-offs between efficiency of development, cost optimization, performance optimization, and platform capabilities forms will continue to be important factors to consider in the mobile application development strategies.
Listening to create your app idea? At WRTeam, we deal with creation of the native and cross-platform applications, and we assist companies in determining the most appropriate strategy to use in terms of their needs. Our professional programmers have provided mobile applications that have been successful in various industries, both in start-ups and enterprises. You can either require the lightning-fast native performance, or you can afford cross-platform coverage, we will be there with you to go through all the steps of the development process. Make your mobile app a reality and contact WRTeam today to get a free consultation.
